Team PlugInIndia have been interacting and working with multiple EV Charging Station manufacturers over the last few months.
In this blog, we share information about Electric Vehicle Supply Unit, Home and Public charging, AC & DC charging, Bharath EV specs and other knowledge and insight gained regarding EV charging.
Did you know electric car's such as the Mahindra e2o or the Nissan Leaf comes with an onboard charger that is built into the car?
Then why do we need a wall mounted box or an EVSE?
The wall charger or charging station is really just a device that safely allows electricity to flow. The EVSE enhances safety by enabling two-way communication between the charging station and the electric vehicle.
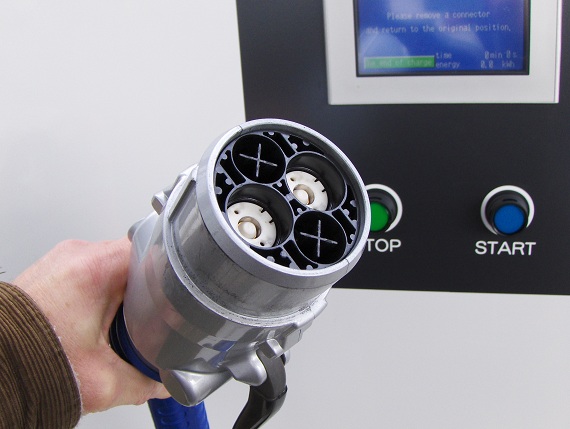
Also EVSE's have a safety lock-out feature that does not allow current to flow from the device until the plug is physically inserted into the car. ARAI and Bharat EV specs recommend using EVSE's to charge any EV safely as compared to using a simple 15 Amp 240 V socket.
Also the current passed to the vehicle is both below the limits of the EVSE and below the limits of what the car can receive.
For example the Mahindra e2o charges (AC Charging) at a rate of 2 kw. And that is the limit at which charging occurs. So even if the EVSE is capable of sending in more power, the car charges at 2 kw. Global EV's like the Nissan Leaf or the Tesla Model S for example can charge at a higher rate upto 22 kw. This enables AC charging at a faster rate.
Also most EVSE's come with added features like
- Authentication
- Integrated payment gateways
- Software for Remote monitoring
So essentially an EVSE is a wall mounted box that - that supplies electric energy to the onboard charger for the recharging of electric vehicle batteries, with lots of intelligence built-in. You can be assured that you are charging your EV in a safe and smart manner.
The home private chargers are generally used with 230V/15A single phase plug which can deliver a maximum of up to about 2.5KW of power. Thus, the vehicles can be charged only up to this rate. The billing for the power is part of home-metering. This will be continued till a policy evolves to charge the home users differently for EV use. Also Bharat EV Specs recommends using the IEC 60309 Industrial connector from both ends.
Public Charging
For charging outside the home premises, Bharat EV standards recommends that the electric power needs to be billed and payment needs to be collected. The power utilities may also want to manage power drawn by these chargers from time to time.
Slow AC charging is the most common method of charging electric vehicles.
An EVSE supplies AC current to the vehicle’s onboard charger which in turn converts the AC power to DC allowing the battery to be charged.
So when you charge your Mahindra e2o or the e2o plus electric car or a Lithium-Ion based e-Scooter using a 15 Amp socket or a smart charger, then you are charging you are - AC charging your EV.
Under AC Charging there are 2 categories of charging
- Normal AC charging
As mentioned above, electric 2-wheelers, 3-wheelers and 4-wheeler vehicles in India has on-board charger that charge at rate of around 2.5kW to 3kW.
These AC 2.5KW or 3KW Chargers could fast charge a 2-wheeler (for a battery with an energy density of 2KWh) in an hour’s time; 4-wheeler or larger vehicles with batteries of 12 KWh or more will be charged in five to six hours.
- Fast AC charging
Global electric cars like the Nissan Leaf or the Tesla have on board chargers with higher power ratings.
This enables AC charging at a faster rate, from 7.7 kw to 22 kw.
AC Plug Connectors
Indian electric cars use the IEC 60309 Industrial Blue connectors and Bharat EV specifications recommend using this plug.
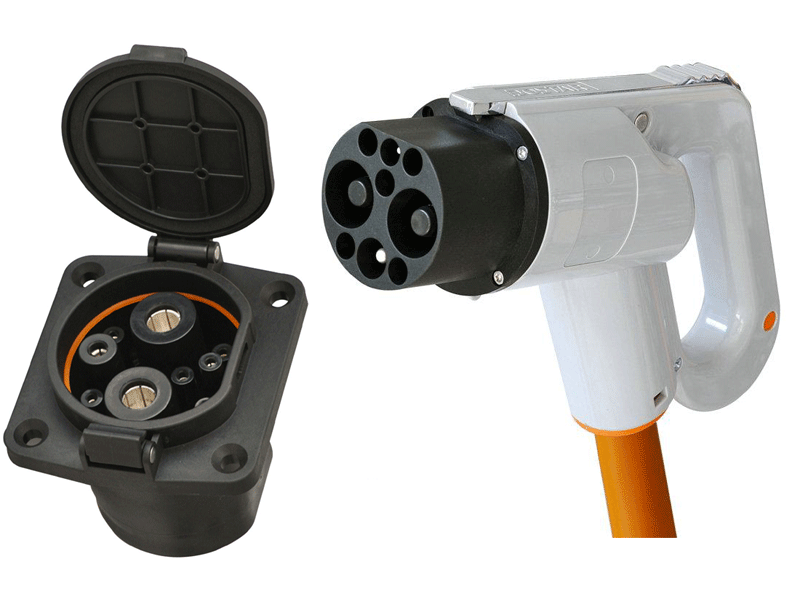
Global EV's use the IEC 62196 Type 2 connector (commonly referred to as Mennekes). This plug was selected by the European Commission as official charging plug within the European Union. It has since been adopted as the recommended connector in countries outside of Europe.
| IEC 60309 Industrial Socket used by Indian e-Rickshaws, Mahindra e2o, Mahindra e2o Plus P6 This is the Bharat EV standard | IEC 62196 Type 2 connector used by Indian and Global EV's electric cars, Mahindra e2o Plus 8, Nissan Leaf, Renault Zoe etc | Simple 3 pin connector coupled with a 15 Amp plug used in Indian e-Scooters |
In this method of charging, DC current is sent to the electric car's battery directly via the DC charge port.
Fast charging’s faster charge rate (usually 50 kiloWatts or more outside India) can supply 100 or more km's of range per hour of charging. A significant fast charging network available should make electric cars more attractive than otherwise, and lead to higher adoption rates.
And having such a network will mean an electric car drivers can take real road trips — blowing up one of the negative electric car stereotypes. (like being be limited to driving a short distance from your home).
Also DC Fast chargers are important for cab companies and corporates who might have a fleet of electric cars.
As per Bharat DC Charging Specifications,
Power rating of fast chargers are
- 10kW/15kW/30kW/50kW or even higher capacity.
- 48V/72V for Indian electric cars like the Mahindra e2o Plus P8, Mahindra e-Verito and upcoming Tata electric cars
- Up to 750V or even higher used by global electric cars like Nissan Leaf and others
Level 1 DC Chargers
Public DC Chargers at output voltage of 48V / 72V, with power outputs of 10 kW / 15 kW with maximum current of up to 200A.
As per the Bharat EV specs, these will be called Level 1 DC Chargers.
Level 2 DC Chargers
Public DC Chargers at output voltage up to 1000V, with power outputs of 30 kW / 150 kW. These will be called Level 2 DC Chargers.
DC Plug Connectors
There are four or so DC Fast Charging connectors currently being used by electric car manufacturers all over the world.
- CHAdeMO – Nissan and other Japanese companies like Mitsubishi
- SAE Combo Charging System (CCS) – (BMW, GM, VW, and other carmakers)
- Supercharger – Tesla standard connector
- GB/T - BYD among other Chinese companies use this. Mahindra and Tata electric cars also use this standard
Bharat EV Charger DC-001 specifications recommend the China based GB/T connector standard. Also Indian electric cars and electric buses use the GB/T port on the vehicles for DC fast charging.
We feel costs could be a major factor in India opting for GB/T compared to CHAdeMO or CCS. Also because car companies are looking to the Chinese and Asian market to increase car sales, it’s possible that whatever fast charging standard China chooses, will, by weight of numbers, become the world standard.
DC Plug Connectors
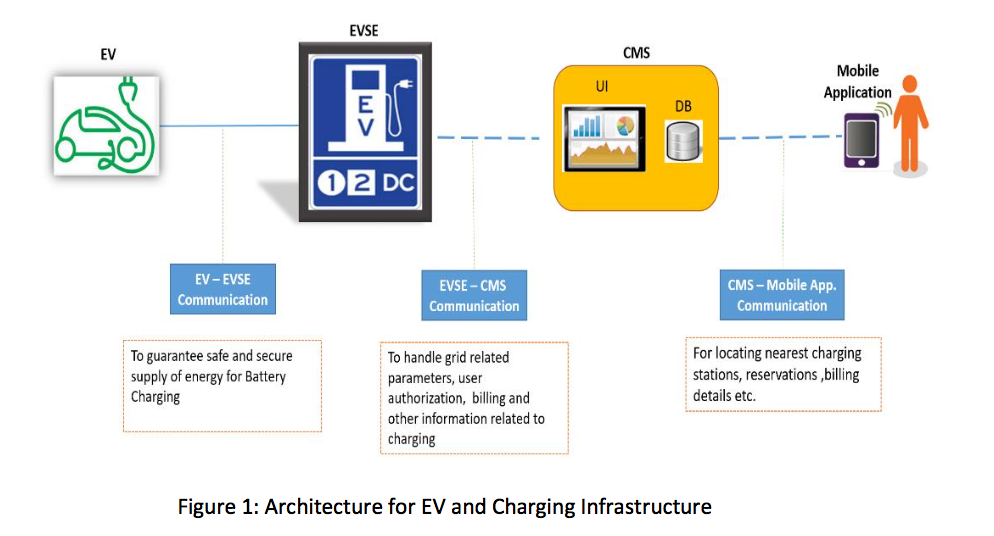
The Bharat EV Specifications also discusses about the communications that need to occur between the EVSE and an electric vehicle.
Also the communication that needs to happen between the EVSE and a remote server.
- The EVSE needs to communicate with BMS of battery pack in EV, to enable it to charge at right rate for maintaining SOC of batteries. Physical layer for this communication will be CAN, as it is commonly used by vehicle manufacturers in India.
- Communication between EVSE and Central management system (CMS) located at power utility company, so as to enable maximum charging rate to be controlled depending upon the rates of grid supply. This will also enable metering at different rates. This is critical as whenever vehicles consume large currents and grid should be able to supply it. This will also enable reservation of chargers by users.
- The communication protocol used will be OCPP. This will be carried on Internet, using wired media or wireless (Wi Fi or GPRS or 3g/4g wireless).
We list some companies that are working hard to get EVSE's into the Indian market. They are also getting their chargers certified by ARAI, Pune.
- MassTech-Controls
A Mumbai based company that has AC and DC chargers. They also have a Bharat EV spec based AC charger. - DrivAMP
A Bengaluru based startup that is developing a Made In India AC charger. - Exicom
A Gurgaon based company that has AC and DC chargers. They won the tender to install around 300 AC chargers in NCR. - Global players also are venturing into Indian market
- Bosch
- ABB
We @ PluginIndia will feature these products in our website and YouTube channel soon.
Having multiple charging protocols is a pain point in the electric vehicle industry. The world is spending more money than necessary to support multiple charging protocols. For example, Tesla Motors is spending lots of money building a proprietary charging network that can only be used by owners of Tesla’s automobiles, while at the same time the charging network operators are spending lots of money to build out fast charging for the other protocols.
We don't want the same thing to happen in India. We dont want a Mahindra or a Maruti or a Tata to develop their own standards.
Thus the need for Bharat EV specifications for AC and DC charging.
We commend our government for stepping up and giving direction to the Indian EV industry.
http://dhi.nic.in/writereaddata/UploadFile/Standardization%20of%20protocol.pdf
Read ARAI's - Electric vehicle conductive AC charging system
https://araiindia.com/hmr/Control/AIS/1212201523221PMEVC_DraftD1_for_website.pdf