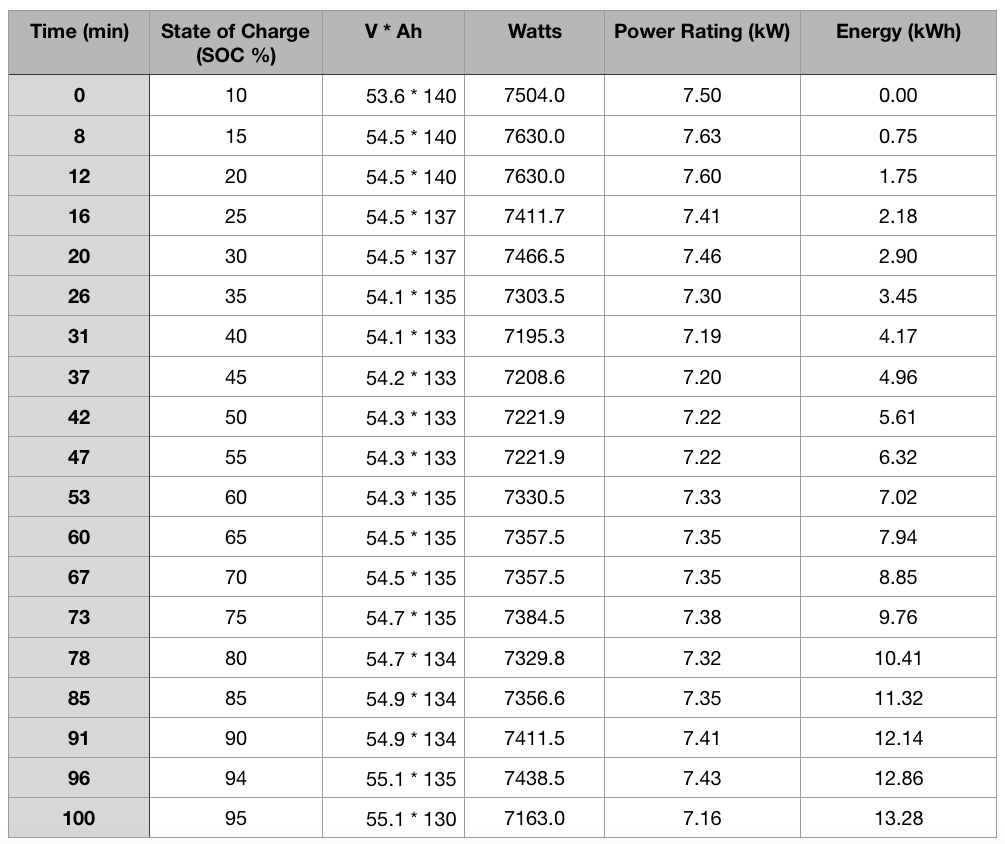
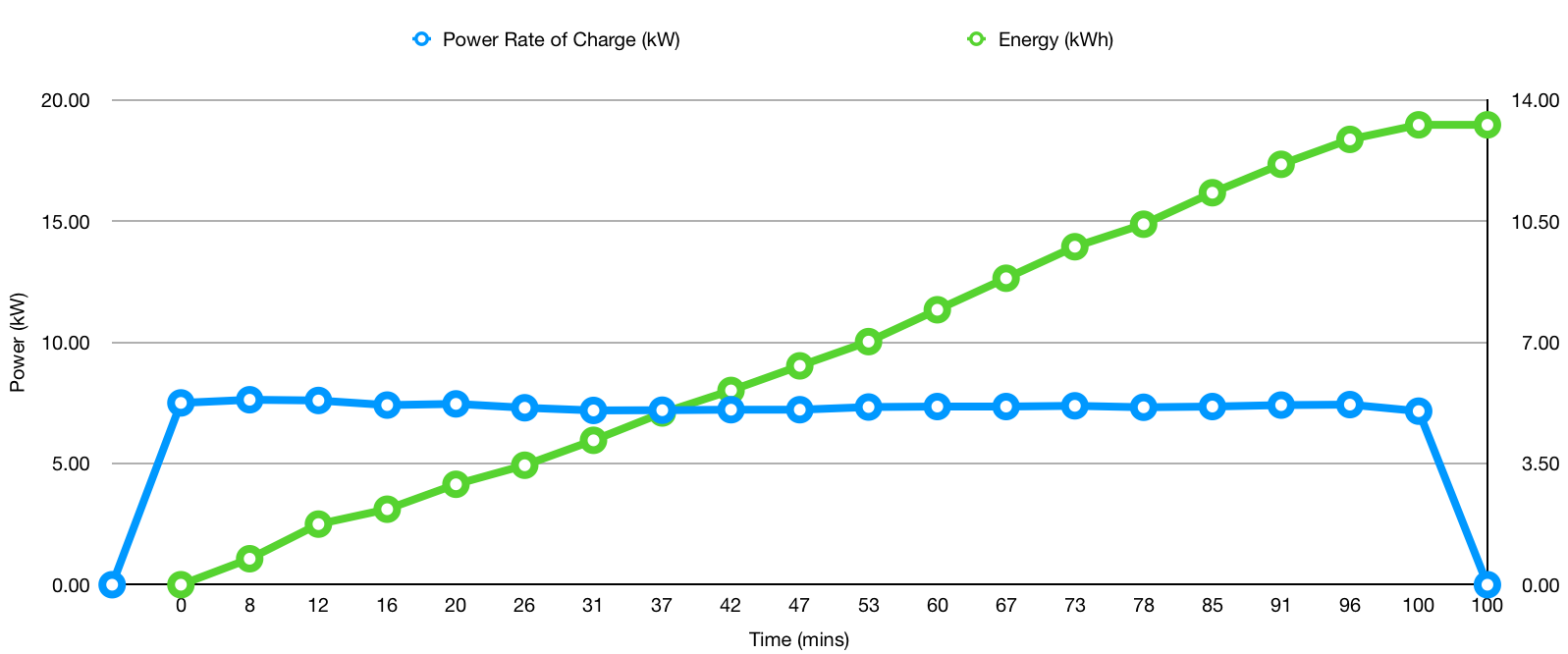
What is the average rate of charging?
How much time does it take to fast charge an Indian electric car?
How much electricity is consumed per session?
Watch the video and check out the numbers in this article.
We show the dash of the e2o plus in a time lapse format from 10% SOC to 95% SOC. The time lapse is be sped up to ensure the video takes 3-4 minutes length. The video also shows Energy Density (kWh) & Rate of Power (kW) in form of a line graph against the time taken to fast charge the car.
Direct current fast charging is used today to speed up the charging process of electric vehicles.
The charging station is directly connected to the vehicle battery. No on-board charger is required for this charging method.
However, the charging stations must be able to adapt to the battery‘s voltage level and the key performance data required for charging (charging state, charging voltage, max. charging current) must be exchanged between the vehicle (battery) and charging station. The
vehicle controls the charging process during this communication exchange, while the charging station controls current and voltage
supply.
High voltage based systems in Electric cars from Nissan Leaf, Hyundai Kona and others are expected to be launched in 2019 and early 2020. These systems operate at voltages up to 850 V and currents up to 200 A, which will offer very different data sets compared to what you see above with current generation low voltage based Indian Electric Cars.
Further Reading
Bharat EV specifications for AC and DC charging - Everything you need to know!